Anatomy Of Ribs : rib cage anatomy : The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs.
Anatomy Of Ribs : rib cage anatomy : The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs.. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They increase in length, curvature and amount of cartilage craniocaudally. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ribs. These three types can then be classified as either typical or atypical. Learn about rib cage anatomy from spinal expert sarah key.
Start studying anatomy of the rib. The ribs are the bony framework of the thoracic cavity. There are twelve pairs of ribs, all of which articulate ribs 3 to 9 are considered typical ribs. The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs. Detailed anatomy of the rib cage | specific articulations.

There are two types of ribs, namely typical and atypical.
Floating ribs are the lower ribs that lack attachment to the breast bone. Anatomical diagram art print human ribcage butterflys instant digital download a4 printable image pdf jpeg unique fun home decor artwork. Learn more on this topic. Ribs eight to ten are the false ribs and are connected to the sternum indirectly via the cartilage of the rib above them. They are twelve in number on either side; Costae are arranged in pairs and articulate with two successive vertebrae. Don't just draw a generic rib cage shape in look for clues from landmarks and muscle attachments that will tell you exactly where the rib cage is. Introduction to the structure of the ribcage and ribs: Start studying anatomy of the rib. They are strong enough to support the skeleton and protect the vital organs in the chest cavity, including the heart, lungs, and spleen. It protects the intercostal space containing the , , and. The vertebral attachment of rib 1 can be found just below the neck and found above the level of the clavicle. Individual ribs have a bony dorsal part, a body of rib, and ventral costal cartilage.
The ribs are a set of twelve paired bones which form the protective 'cage' of the thorax. Ribs 2 through 7 have a more traditional appearance and become longer and less curved as they progress downwards. Coastal cartilages are joined to the. Try to be as accurate as you can with them. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity.
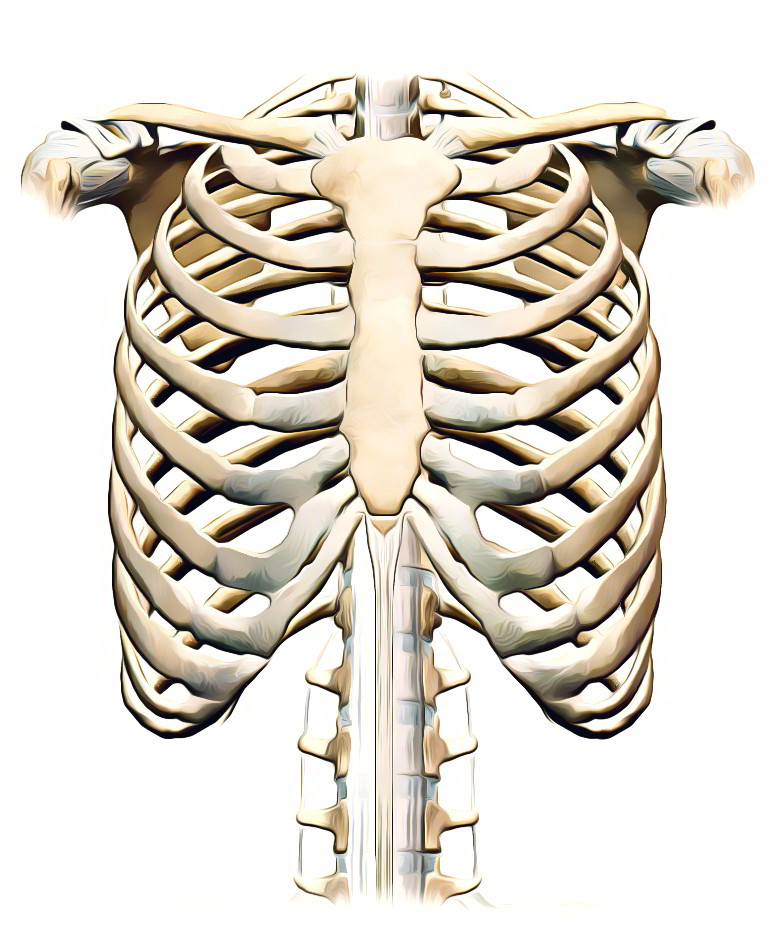
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ribs.
Costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. It protects the intercostal space containing the , , and. There are twelve pairs of ribs, all of which articulate ribs 3 to 9 are considered typical ribs. Learn the true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs, as well as the difference between in this anatomy lesson, i'm going to cover the rib bones, also called costae in latin. They are strong enough to support the skeleton and protect the vital organs in the chest cavity, including the heart, lungs, and spleen. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. In vertebrate anatomy, ribs (costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage. The ribs are a set of twelve paired bones which form the protective 'cage' of the thorax. Try to be as accurate as you can with them. Don't just draw a generic rib cage shape in look for clues from landmarks and muscle attachments that will tell you exactly where the rib cage is. The ribs partially enclose and protect the chest cavity, where many vital organs (including the heart and the lungs) are located. Costae are arranged in pairs and articulate with two successive vertebrae.
Individual ribs have a bony dorsal part, a body of rib, and ventral costal cartilage. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ribs. The ribs stretches posteriorly from thoracic vertebrae to the anterior lateral edges of the sternum. Major landmarks of a typical rib are the following: In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity.

The ribs stretches posteriorly from thoracic vertebrae to the anterior lateral edges of the sternum.
Start studying anatomy of the rib. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. The rib cage, shaped in a mild cone shape and more flexible than most bone sets, is made up of varying elements such as the thoracic vertebra, 12 equally paired ribs, costal cartilage, and held together anteriorly by the sternum. These three types can then be classified as either typical or atypical. The first seven are connected behind with the vertebral column and. The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs. The ribs are the bony framework of the thoracic cavity. The first seven are connected behind with the vertebral column. In vertebrate anatomy, ribs (costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage. There are two types of ribs, namely typical and atypical. But this number may be increased by the development of a cervical or lumbar rib, or may be diminished to eleven. Costae) are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. They are strong enough to support the skeleton and protect the vital organs in the chest cavity, including the heart, lungs, and spleen.
Komentar
Posting Komentar